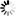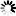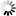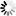FlowTraq provides a powerful ability to create and manage users and their access to flow data. Individual users can be minutely restricted in their access to flow data, enabling FlowTraq to be used in multi tenant systems where more than one organization uses the same backend FlowTraq deployment. Flow data will be neatly separated based on boundaries that you configure.
Each user has access to their own customizable dashboard, and settings are applied on a per-user basis. FlowTraq separates user accounts into two distinct groups:
- Administrators
Administrative users can create and delete user accounts, manage traffic groups, modify the configuration of the FlowTraq server, and limit which traffic each regular user has access to. Administrators belonging to the Main partition (CID 0) are System Administrators. Administrators in other partitions are Partition Managers.
- Users
Regular users can analyze traffic, view alerts and quickviews, and customize their dashboard.
In addition to local user management, FlowTraq can also authenticate users through one or more LDAP servers. FlowTraq always attempts to authenticate users in the local user database first, before attempting authentication with an external LDAP server. You may map LDAP user groups to both the regular FlowTraq users group, and the FlowTraq administrative account group.
This section describes the different kinds of FlowTraq user accounts, and includes information on how to change user passwords, add and remove users, and grant and revoke privileges.
FlowTraq has two kinds of user accounts: Administrative Users or "Administrators" and Unprivileged Users .
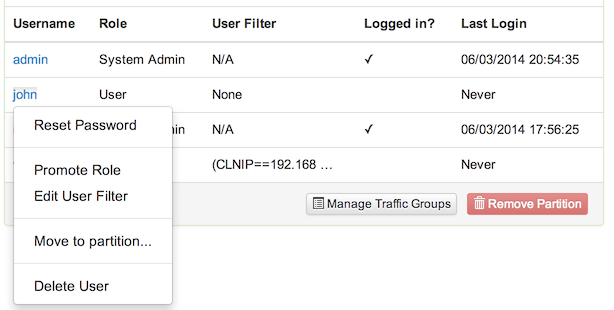
Administrators (such as the default admin account) have access to the Administration/User page:
A checkmark in the Active column indicates if a user is currently logged in. It is not possible to delete users that are currently logged in.
The Role column indicates if a user is an administrator (either System Admin or Partition Manager) or a regular user.
The User Filter column indicates if an access control filter is active, restricting this user to specific partitions and/or traffic groups.
A password reset link is provided in the context menu. It is not possible to change the password for externally authenticated users (LDAP) through FlowTraq.
An Administrator may create new users from the Partition Actions menu. From the user context menu, an Administrator may remove user accounts, make other users into Administrative Users (or remove that status), move users among partitions, add user filters, and reset user passwords.
Administrators can also set up access controls for each unprivileged user to restrict what sessions they can see when doing analytics. For more information on how to set up user access control, please see Section 4.2.1.3, “User Filter Control”.
![[Important]](../common/images/admon/important.png) | Important |
|---|---|
Upon first login, you should immediately change the password for |
You can grant and revoke administrative privileges by taking the following steps:
Log in as an Administrator.
Open the Administration/User page.
Select the user whose privileges you wish to change by clicking their username. If the user is not visible, ensure that you have administrative permissions for the correct Partition.
Select Promote Role from the context menu to grant administrative privileges.
Select Demote Role from the context menu to revoke administrative privileges.
![[Important]](../common/images/admon/important.png) | Important |
|---|---|
You cannot revoke your own administrative privileges. (This is to prevent the system from getting into a state where there are no administrators.) |
![[Important]](../common/images/admon/important.png) | Important |
|---|---|
You cannot grant or revoke administrative privileges of users that are externally authenticated (LDAP). You must change their group membership on your LDAP server instead. |
You can add and remove users by taking the following steps:
Log in as an Administrator.
Open the Administration/User page.
To remove a user:
Select the user whose privileges you wish to change by clicking their username.
Select Delete from the context menu.
![[Important]](../common/images/admon/important.png) | Important |
|---|---|
You may not delete a user that is currently logged in. |
![[Important]](../common/images/admon/important.png) | Important |
|---|---|
Deleting an externally authenticated user will only delete their settings. To prevent an LDAP authenticated user from accessing FlowTraq you must disable their access on your LDAP server. |
To add a user:
Open the Administration/User page.
Click the Action button at the upper right of the partition to which that user should belong, and select Create New User
You will be asked to enter your administrative password, and a username and password for the new user. Select Add to create the new FlowTraq user account.
![[Important]](../common/images/admon/important.png) | User Name Rules |
|---|---|
User names must conform to the following rules:
|
FlowTraq provides a user access control mechanism which permits an administrator to decide which sections of the network an unprivileged user may see. Primary access control is performed through assignment to partitions, but individual users within a partition may be further restricted, or users in the main partition may be restricted on a partition-by-partition basis. This is accomplished by setting a User Filter for each unprivileged user. On login, the unprivileged user will only see sessions which match the User Filter. This is especially useful in multi-tenant/managed-services environments.
To set a user's User Filter, take the following steps:
Log in as an Administrator.
Open the Administration/User page.
Click the name of the appropriate user. (Note that setting a User Filter on an Administrator is not permitted, as such a user can easily revert the setting.) Select Edit User Filter.
The partitions and traffic groups that are potentially visible to the user are displayed. A user may be given full access, partial access, or no access to individual partitions. If partial access is selected, the user's view is restricted according to the specific traffic groups selected within that partition. If two traffic groups communicate with each other, a user with visibility into either traffic group will see the selected session.
Set the user's filter and click "Save".
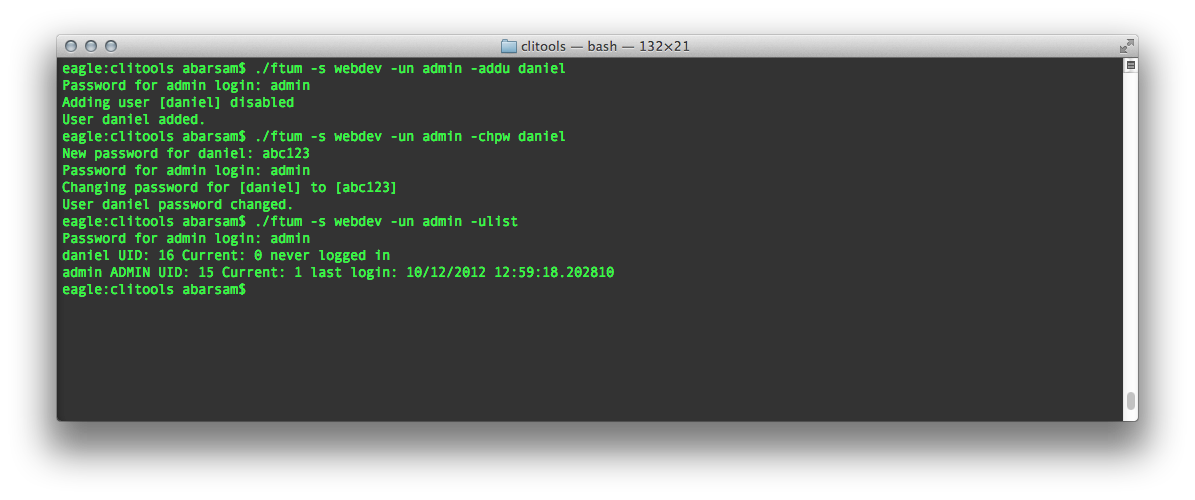
To manage users, use the ftum command. Administrative credentials are required to create, or modify user accounts.
You must specify a FlowTraq Server to connect to and supply login details.
In addition to the connection and login parameters, ftum accepts the following parameters:
Table 4.2. User Management Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
-chpwd USERNAME PASSWORD
| Change password for user USERNAME to PASSWORD . You must log in as USERNAME to perform this action for yourself, or as an administrator to perform this action for an arbitrary user. |
-addu USERNAME PASSWORD
| Add a new user, USERNAME , with initial password PASSWORD . You must log in as an administrator to perform this action. |
-delu USERNAME
| Delete user USERNAME . You must log in as an administrator to perform this action. It is not possible to remove a user that is currently logged in. |
-admin USERNAME
| Grant administrative privileges to user USERNAME . You must log in as an administrator to perform this action. |
-noadmin
| Revoke administrative privileges from user USERNAME . You must log in as an administrator to perform this action. |
-ulist
| Print the list of users. You must log in as an administrator to perform this action. |
-getpref USERNAME KEY
| Request a user-specific parameter KEY for user USERNAME. |
-setpref USERNAME KEY
| Set a user-specific parameter KEY for user USERNAME. Some parameters cannot be set by the user themselves, such as userfilter which controls what traffic a regular user may analyze. Other parameters, such as colorscheme can be modified by the user themselves.
|
-cid CID
| Specify the partition selection when moving users or when performing administrative actions |
-chcid USERNAME
| Move an existing user to a new partition (use with -cid to specify the destination partition) |
For example, to add a new user (with the -addu option) and set the initial password (with the -chpwd option), take the following steps:
FlowTraq supports external user authentication through the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol. This means that you can quickly grant user or administrative access to your FlowTraq server or cluster by mapping LDAP groups to FlowTraq roles. When users attempt to authenticate with a FlowTraq server, their credentials are first checked against the local FlowTraq user account database. If authentication fails, up to 4 LDAP servers can be queried to authenticate the user.
Using LDAP for authentication allows for a convenient way to manage access for many users at the same time from directory servers such as Active Directory. FlowTraq will treat these user accounts as external, although some local controls may still be applied. User settings such as dashboard layout and colorscheme will be stored on the FlowTraq server. It is also possible to apply user access controls to regular users, see Section 4.2.1.3, “User Filter Control”.
![[Important]](../common/images/admon/important.png) | Important Limitations of LDAP users |
|---|---|
Externally authenticating users comes with a couple of important limitations:
|
An LDAP server is configured in the flowtraq.conf FlowTraq server daemon configuration file. After adding or removing a configuration, the FlowTraq daemon process must be sent a HUP signal to trigger a reconfiguration. Below is an example of an LDAP configuration:
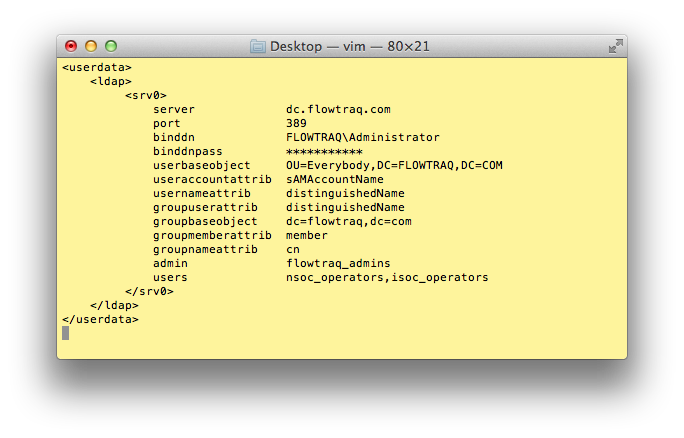
You may configure up to four LDAP server blocks srv0, srv1, srv2, and srv3, which will be searched in numerical order.
-
server The IP address or hostname of the LDAP server that FlowTraq should connect to.
-
port The TCP port of the LDAP service (389).
-
binddn The distinguished name of the LDAP account that is used to browse the directory service. This account must have sufficient privileges to query the LDAP server for users and groups. It is used to validate that users are valid members of the directory, and belong to groups that are mapped to FlowTraq users or administrators.
-
binddnpass The password for the LDAP account that is used to browse the directory service.
-
userbaseobject This is the base object that holds all the relevant user accounts in the directory. This object is searched for the credentials provided by the users to FlowTraq when they log in. Usually:
OU=Users,DC=FlowTraq,DC=com, or simplyDC=FlowTraq,DC=com.-
useraccountattrib The attribute of user objects that users will use to identify themselves to FlowTraq. You may pick any attribute that identifies a user in your directory. This is usually
sAMAccountName.-
usernameattrib This is the attribute of user objects that FlowTraq will search for and use to offer the credentials to the LDAP server for authentication. This is usually an attribute that uniquely identifies the user in the domain. A good value is
distinguishedName.-
groupuserattrib This is the attribute of user objects that is used in to identify membership in groups on your directory server. Often the
distinguishedNameof the user is used to identify them as members of a specific group.-
groupbaseobject This is the base object that holds all the relevant group accounts in the directory. This object is searched for the groups provided by the user and admin mappings given by the
adminandusersparameters, to establish if the user who is attempting to login is a member of an appropriate LDAP group. Usually:OU=Groups,DC=FlowTraq,DC=com, or simplyDC=FlowTraq,DC=com.-
groupmemberattrib This is the attribute of group objects that is used to list all the groups member users. Usually:
member.-
groupnameattrib This is the attribute of group objects that is used to identify them in the
adminandusersmappings. Usually:cn.-
admin List all the LDAP groups that should have administrative access to the FlowTraq daemon. You may list up to 8 groups.
-
users List all the LDAP groups that should have regular user access to the FlowTraq daemon. You may list up to 8 groups.
![[Important]](../common/images/admon/important.png) | Important |
|---|---|
Note that it is possible to configure the same LDAP server multiple times, but with a different group mapping in each configuration. |
FlowTraq supports external user authentication through the Terminal Access Controller Access-Control System Plus (TACACS+) Protocol. When users attempt to authenticate with a FlowTraq server, their credentials are first checked against the local FlowTraq user account database. If authentication fails, the specified TACACS+ server is be queried to authenticate the user.
If a user account authenticates for the first time through TACACS+, FlowTraq will treat that account as external, although local controls may still be applied. User settings such as dashboard layout and colorscheme will be stored on the FlowTraq server. It is also possible to apply user access controls to regular users, see Section 4.2.1.3, “User Filter Control”, or to make an external user an administrator.
A TACACS+ server is configured in the flowtraq.conf FlowTraq server daemon configuration file on the FlowTraq portal. After adding or removing a configuration, the FlowTraq daemon process must be restarted or sent a HUP signal to trigger a reconfiguration. Below is an example of a TACACS+ configuration:
<userdata> <tacacs> <srv0> server 192.168.2.70 port 49 secret MyPassw0rd </srv0> </tacacs> </userdata>
-
server The TACACS+ authentication server which FlowTraq should contact for user authentication.
-
port The TCP port on which FlowTraq should contact the specified TACACS+ service.
-
secret The shared secret you have configured on your TACACS+ system, to be used alongside user credentials.